

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/lumbar_vertebrae-5b6ef83e46e0fb005025872a.jpg)
tough collagenous fibers - reinforce joint capsule - bind articular ends- May be inside fibrous layer of capsule or outside- Prevent excessive movement at the joint- Relatively inelastic 2 layers of dense connective tissue- Holds together bones of synovial joint- Its fibers attach to periosteum Articular cartilage- Tubular joint capsule- Ligaments- Synovial membrane- Synovial fluid- Menisci- Burase
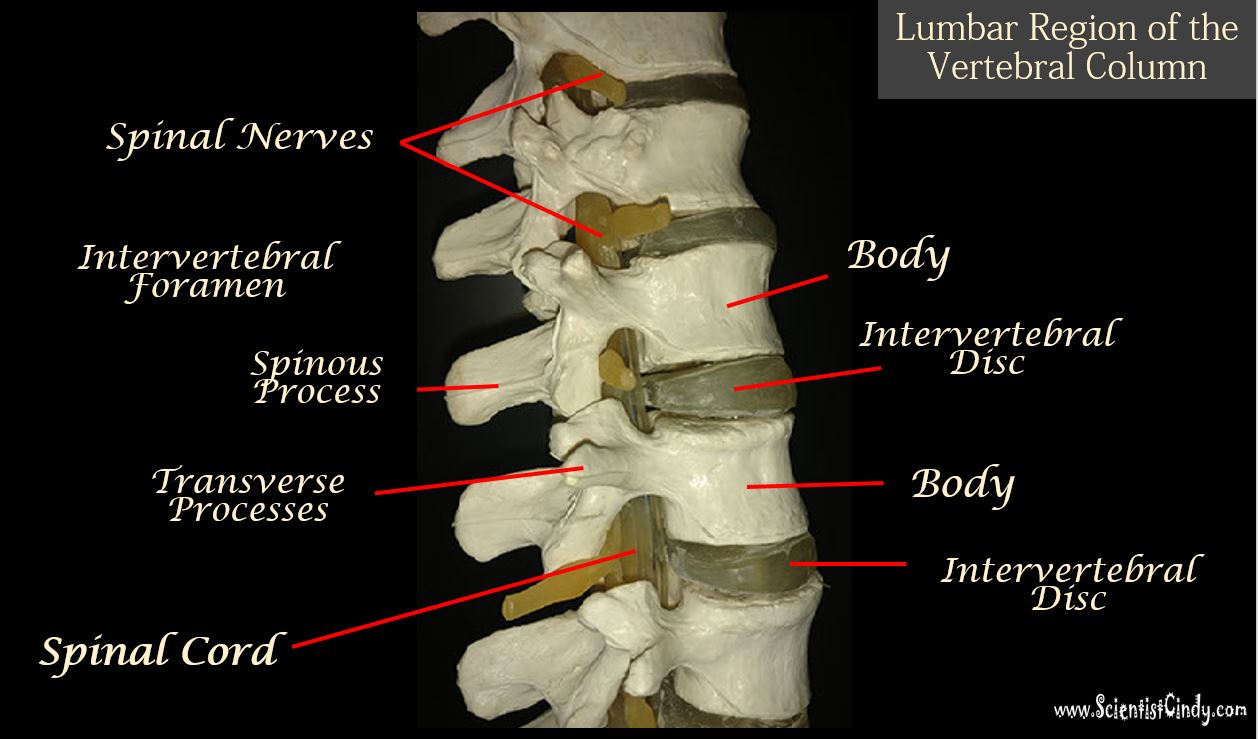
Most jointsAllow free movement - diarthroticConsist of:- Articular cartilage- Joint cavity or capsule - Synovial membrane -secretes synovial fluid Hyaline cartilage untie bones-Temporary- cartilage band- epiphyseal plate-Permantet- between manubrium & 1st rib-SynarthroticĪrticular surface covered by thin hyaline and fibrocartilage-Symphysis pubis (pelvis) & intervertebral disks (amphiarthrotic) Hyaline of fibrocartilage unite bonesTwo Types:a. Gomphosisīones bound by interosseous ligament- ampthriarthoricīetween the flat bones of skull only- sutural ligaments- synarthroticįormed by union of cone-shaped bony process in a bony socket-synarthrotic Joints between the pubic bones of the pelvis & vertebraeīones united by fibrous tissue - 3 types:a. Site where two or more bones meet andenable movementīy the type of tissue that binds them together and also by grouped according to the range of movement possible at the junctions betweenbones.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
